Legacy SIEM solutions like Splunk are valuable for analyzing machine-generated data but their volume-based pricing can lead to high costs and difficult decisions for security teams. Snowflake offers an alternative with flexible pricing, unlimited data storage, and cost-saving data ingestion and retention options. Real success stories demonstrate remarkable cost savings with Snowflake.
Category: Professional
Snowflake’s New Python API Empowers Data Engineers to Build Modern Data Pipelines with Ease
Snowflake recognizes the shift to Python as the preferred language for data teams and introduces the Python API to bridge the gap. The API aims to streamline workflows, enhance developer productivity, and simplify data pipeline management. By prioritizing the developer experience, Snowflake empowers users to leverage Python within Snowflake for efficient, data-driven solutions across various workloads.
Microsoft Fabric Co-Existing as Semantic Layer with Power BI & Snowflake
Customers have transitioned to Snowflake on AWS and Power BI on Azure, consolidating reporting/analytics platforms. This has improved operations but led to performance and cost challenges, hindering self-data service. Creating a semantic layer in Microsoft Fabric with Snowflake Mirroring is proposed as a solution, offering better performance and cost savings.

Migrate Business Logic from Database to Application for Faster Innovation and Flexibility
The article discusses the migration of business logic from the database layer to the application layer. It emphasizes the benefits of migrating from PL/SQL to Java for scalability, flexibility, support, and cost savings. Ispirer’s SQLWays Wizard tool streamlines the migration process, automating assessment, code conversion, and report generation, facilitating a smooth transition.

Unveiling SEO Treasures: Identify Keywords Beyond Your Competitors’ Reach
Keywords are crucial for SEO, bridging what users search for and web content. The competition is fierce, requiring extensive research and advanced strategies like long-tail and semantic keyword analysis. Niche keywords offer lower competition. Utilize tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz Keyword Explorer to gain a competitive edge. Continuous exploration and optimization are necessary for SEO success.
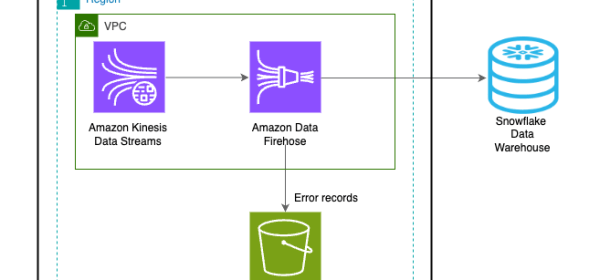
Uplevel your data architecture with real- time streaming using Amazon Data Firehose and Snowflake
Streaming data is crucial in today’s fast-paced world, and Snowflake’s Snowpipe and Snowpipe Streaming provide options to bring in data from sources like Amazon Kinesis Data Streams or Amazon MSK. Amazon Data Firehose integration with Snowpipe Streaming allows real-time, cost-effective, and serverless data delivery to Snowflake, enabling advanced analytics within seconds.

A Guide to API Monitoring: Strategies for Keeping Your Services Reliable
APIs are vital for digital interactions, but they can encounter issues. Monitoring them is crucial for smooth operations and user satisfaction. Key metrics for monitoring include response time, success rate, error rates, traffic, latency, throughput, and availability. Effective strategies involve alerts, health checks, log analysis, benchmarking, user-centric monitoring, security monitoring, performance trends analysis, and feedback loop.

Bringing DevOps Automation to Legacy Systems
Many organizations adopt DevOps for conventional applications using automation tools like Infrastructure-as-Code and Configuration-as-Code. Integrating legacy systems with automation involves innovative practices like cloud migration, containerization, machine learning, and changing organizational mindset. This helps improve legacy software’s flexibility and quality, reducing costs, albeit with unique challenges compared to modern software automation.

Modern Application Management Requires Deeper Internet Visibility
Most IT teams struggle with limited visibility into application performance due to distributed applications, leading to blind spots caused by third-party services, device-level issues, and various platforms. Integrating Internet Performance Management (IPM) with APM/observability platforms empowers DevOps to troubleshoot and manage network operations effectively, reducing stress and toil significantly.

The Evolution of the Kubernetes Gateway API
The article discusses the Kubernetes Gateway API, a key component of Kubernetes enabling standardized inbound traffic management. It enhances cloud and hybrid environment integration, supports multi-cluster setups, and future improvements in load balancing, traffic management, and auto-scaling. The API aims to enhance scalability, performance, and community collaboration within Kubernetes ecosystems.

Why is observability so expensive?
The article addresses the rising concern about observability costs in the current economic climate. It discusses the evolution of modern observability, the root cause of the cost crisis, and proposes a new approach to observability. The author anticipates a new golden age of observability with the end of excess and the rise of control plane-driven infrastructure.

Best Practices and Strategic Insights to Dockerizing Your Linux Applications
Docker revolutionizes software development and deployment with its containerization approach, offering consistency, isolation, and resource efficiency. The guide covers Dockerizing applications on Linux, including installation, best practices, security, deployment strategies, and real-world examples from industry leaders like Spotify and Netflix. Embracing Docker empowers developers and organizations to innovate in cloud computing and microservices architectures.
Azure OpenAI and Call Center Modernization
Azure OpenAI is transforming modern call centers, tackling challenges like high call volume and long wait times. The architecture integrates AI layers with existing systems to assist human agents, improve customer interactions, and secure sensitive data. Implementation of robust security measures and best practices ensures a proactive, inclusive security framework.
KPIs – Enterprise Journey from Technology to Business
This blog post emphasizes the importance of well-defined business KPIs for successful cloud transformation. It details a fictional company’s journey, recommending a phased approach to adopting KPIs – starting with technology KPIs, then introducing business KPIs, and finally evolving to track business KPIs over time. The authors are AWS experts with extensive industry experience.
