The need for Cloud-Access Security Brokers
As more applications are being delivered as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and APIs are expanding exponentially within enterprise environments, business application security is at the forefront of cyber security. Many companies have several applications deployed throughout their infrastructure with a lack of visibility and control to ensure secure configurations are applied. In order to effectively manage risk, companies need to review and determine where their applications live, how these applications are deployed, what guardrails are in place, what their role is in the Shared Responsibility of the SaaS application, and if they are being monitored and remediated. With applications being integrated with other services the company is using, the breach of one single application can lead to a major security incident. As an example, a misconfigured application can leave a gap that an adversary can exploit and gain access to other applications which then could cause a major breach. Application-security-related incidents and breaches are gaining traction because of the overall growth within application infrastructure. To back that statement up with statistics, I will reference the report posted by Cyentia Institute titled “The State of the State of Application Exploits in Security Incidents”. When we put these trends into perspective, we can see how applications are affecting the threat landscape we encounter in cyber security today:
Based on the findings presented in the report, a conclusion can be drawn that applications pose a substantial risk. In return, that should trigger an increased awareness around applications and how they are being secured throughout all environments. With these daunting statistics, there needs to be clear direction and drive towards remediating gaps within deployed applications. There are many options available with different security capabilities that create a competitive space to find the right fit for your specific organization. One key factor is that the security solution must be able to encompass all application deployments in many different types of environments while applying secure configurations.
The intent of this blog post is to cover a specific set of security capabilities that can be deployed using the
cloud-native Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) when protecting applications. We will be discussing application governance, but first taking a step back to provide some additional context.
Microsoft native CASB
Microsoft provides a complete end-to-end solution so whether your application lives on-premise or in the cloud, you can leverage existing infrastructure to enrich the data sets. Microsoft’s native CASB also spans over other cloud providers to capture multi-cloud application deployments. This opportunity especially comes in handy if you are already in possession of Microsoft 365 E5 licenses. Defender for Cloud Apps is covered under an M365 E5 license. Should you have Microsoft 365 E3 licenses, you would need add-ons for the full coverage. With Microsoft 365 E5 licensing, you can increase the return of investment (ROI) without having to find additional funds for a new security platform. Defender for Cloud Apps provides a single pane of glass that encompasses all your applications no matter where you are in your current cloud journey.
Should this be your first-time encountering Defender for Cloud Apps (or a CASB), there are a few basic concepts that should be understood. Some of these concepts are covered throughout this blog post; however, I want to start with a quick introduction. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, formerly Microsoft Cloud App Security (MCAS), became generally available on April 6th, 2016. During that timeframe, Defender for Cloud Apps has grown into a robust CASB. Defender for Cloud Apps is recognized as a leader by Gartner® when mapped to the Magic Quadrant. This cloud-native CASB is a very competitive product in comparison to similar tools in its category. When leveraging the Microsoft Defender suite and Azure AD, these tools work seamlessly together adding context and optimizations.
Security managers, directors, and CISOs have asked me some of the following questions in the past.
What will be the level of effort (LOE) to deploy and maintain this tool at scale while supported by current staffing?
Regarding the level of effort with deployments, Microsoft offers options right out of the box. For example, Policy templates are one of the options that can be adjusted and/or applied with very little effort. We can also find plug-and-play features available to be deployed with ease when navigating to the settings and adjusting the toggle.
Will the current security staff have to go through extensive training to gain experience that might take away from other tasks?
Regarding training objectives, Microsoft has articles pinned in many places as you move around within the portal. This makes it easy for staff to get more familiar when pulling up an article to learn more about specific setting(s) when needed.
“Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps natively integrates with leading Microsoft solutions and is designed with security professionals in mind. It provides simple deployment, centralized management, and innovative automation capabilities.” – Microsoft
When navigating to the legacy portal page, it begins at the dashboard. On the left pane you have four additional categories listed; Discover, Investigate, Control, and Alerts.
When using Defender for Cloud Apps, Application Governance is a good way of tightening controls around apps. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is an agentless CASB, meaning we utilize integrations for remediations to be actioned and the CASB itself does not have any control to govern the applications as a standalone tool. We need to keep in mind that it is not the enforcer, but rather an evaluator, letting all your other tools do the actual enforcement action.
Reviewing what integrations can be leveraged is of utmost importance when planning to govern applications. First determine what data sources can be brought in, the current identity provider(s) in use, and specific app connectors. Once in place then the governance policies will be actionable. Below there are two examples that further expand on this.
Example 1: To set up applications to be sanctioned or unsanctioned you first need to leverage your current toolsets such as a secure access service edge (SASE) solution, an edge firewall, or if using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (Microsoft native XDR), that is also an option. These data sources will action requests from an ingress/egress perspective once the signal from Defender for Cloud Apps informs to block or allow. If the goal is to utilize the sanction/un-sanction option with applications, you have to work with a specific data source that can manage the enforcement action.
Example 2: Defender for Cloud Apps Conditional Access App control apps also would need an integration for enforcement. The governance aspect in scope being access and session policies to enforce control over apps. Once again Defender for Cloud Apps will not enforce the action for that we would need to look towards an identity provider (IdP) to help us out. We know Azure AD, under the Microsoft Entra suite, is a native IdP that works directly with Defender for Cloud Apps. Within Azure AD, create a conditional access policy pointing to the custom access or session policy in Defender for Cloud Apps. This can also be deployed to on-premise applications with an application proxy in Azure AD. If another IdP than Azure AD is being utilized, then configure SAML 2.0 or OpenID Connect and connect the applications. Where the application resides, and the authoritative source for identities, will determine the specific integration parameters. Integrating these control policies will assist with tightening down the who, what, and where pertaining to your applications. Policy configurations in Defender for Cloud Apps are very granular, and depending on the use case you can set up these policies as specific or broad as you want. If you want to allow only certain users from a specific range of IP addresses to access certain applications, use access policies. If looking to limit what actions/activities are allowed, then it can be done by adding in a session policy.
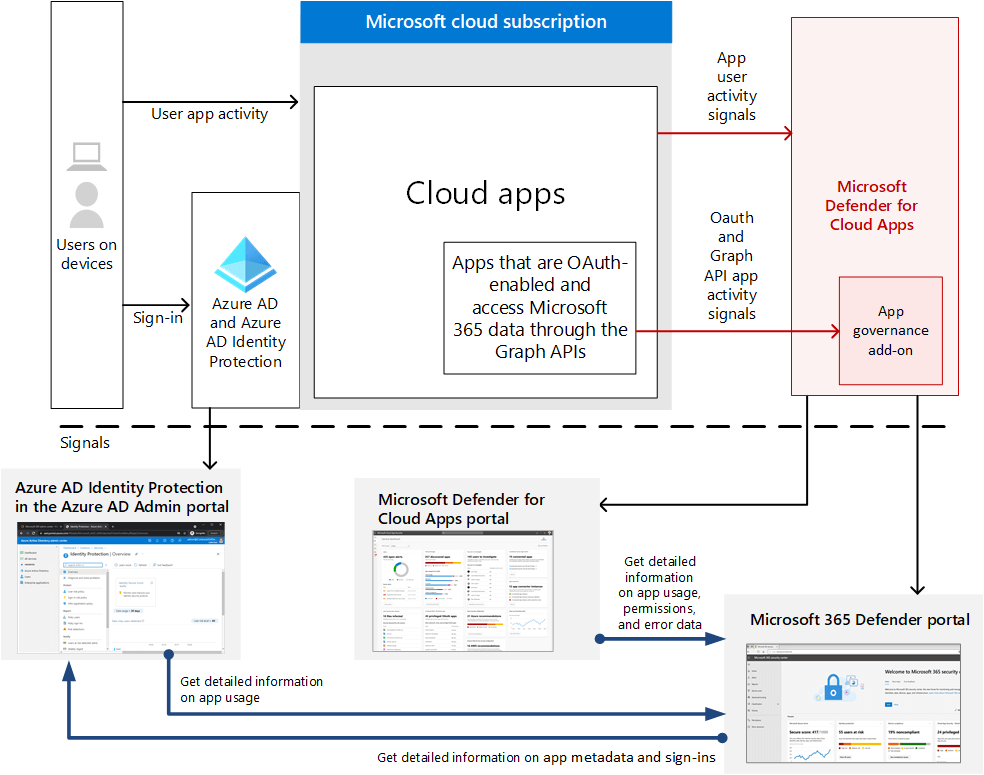
Microsoft is always adding in new enhanced benefits while consolidating and integrating their tools. Defender for Cloud Apps falls under the M365 Defender suite, but as of the time of writing, it also has its own separate portal available. Some of the features are starting to populate the M365 Defender portal giving a centralized view over all your applications, endpoints, emails, and identities. There are new features and functions currently released that pertain to Application Security. Recently Microsoft added security posture management (SSPM) in preview so that customers can gauge additional visibility and remediate potential gaps within their application footprint. Microsoft has also added another layer to application governance itself releasing a new app governance add-on to provide additional control aspects to your applications. This add-on works with Azure AD and Defender for Cloud Apps to stop app usage when analyzing data usage, permissions, and anomalies pertaining to the apps in scope. Below is an architecture diagram that showcases the lifecycle this add-on delivers:
In conclusion: Defender for Cloud Apps governs applications by leveraging data sources to enforce policies and settings. The features we covered include sanctioning or unsanctioning apps, setting up granular policies to define access and session perimeters using an IdP, and new add-on capabilities released providing additional control objectives on demand.
— This blog post is not meant as a configuration guide, or to fit exact scenarios as there are dependencies that could change the desired outcome which depends on a broad set of items. This is a general overview of features that is in place and currently supported by Microsoft.–
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from The Guiding Point | GuidePoint Security authored by Thomas Lysaa. Read the original post at: Original Post>
August 25, 2022
The need for Cloud-Access Security Brokers
As more applications are being delivered as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and APIs are expanding exponentially within enterprise environments, business application security is at the forefront of cyber security. Many companies have several applications deployed throughout their infrastructure with a lack of visibility and control to ensure secure configurations are applied. In order to effectively manage risk, companies need to review and determine where their applications live, how these applications are deployed, what guardrails are in place, what their role is in the Shared Responsibility of the SaaS application, and if they are being monitored and remediated. With applications being integrated with other services the company is using, the breach of one single application can lead to a major security incident. As an example, a misconfigured application can leave a gap that an adversary can exploit and gain access to other applications which then could cause a major breach. Application-security-related incidents and breaches are gaining traction because of the overall growth within application infrastructure. To back that statement up with statistics, I will reference the report posted by Cyentia Institute titled “The State of the State of Application Exploits in Security Incidents”. When we put these trends into perspective, we can see how applications are affecting the threat landscape we encounter in cyber security today:
Source:
https://library.cyentia.com/report/report_007733.html “Cyentia analyzed Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) with its tens of thousands of security incidents from scores of diverse sources each year. There were
4,862 incidents (17% of all incidents) fitting under Application Security in the 2021 report and
1,384 were confirmed data breaches (26% of all breaches). That ranks web application attacks #2 for both incidents and breaches.”
Based on the findings presented in the report, a conclusion can be drawn that applications pose a substantial risk. In return, that should trigger an increased awareness around applications and how they are being secured throughout all environments. With these daunting statistics, there needs to be clear direction and drive towards remediating gaps within deployed applications. There are many options available with different security capabilities that create a competitive space to find the right fit for your specific organization. One key factor is that the security solution must be able to encompass all application deployments in many different types of environments while applying secure configurations.
- APP Remote Control: Easily control your home...
- Voice Control: Smart plugs that work with Google...
- Easy Setup: It takes less than two minutes for the...
- Other Features: Diverse timer scheduling...
- 7*24 Customer Service: If you encounter any issues...
- BETTER INSIDE AND OUT – Entertainment is more...
- VIBRANT SIGHTS, FULL SOUND – Content on Prime...
- SMART HOME, SIMPLIFIED – Pair and control...
- STAY IN THE LOOP – Video call hands-free using...
- SHOW OFF YOUR GOOD TIMES – Amazon Photos turns...
Last update on 2024-04-05 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
The intent of this blog post is to cover a specific set of security capabilities that can be deployed using the Microsoft cloud-native Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) when protecting applications. We will be discussing application governance, but first taking a step back to provide some additional context.
Microsoft native CASB
Microsoft provides a complete end-to-end solution so whether your application lives on-premise or in the cloud, you can leverage existing infrastructure to enrich the data sets. Microsoft’s native CASB also spans over other cloud providers to capture multi-cloud application deployments. This opportunity especially comes in handy if you are already in possession of Microsoft 365 E5 licenses. Defender for Cloud Apps is covered under an M365 E5 license. Should you have Microsoft 365 E3 licenses, you would need add-ons for the full coverage. With Microsoft 365 E5 licensing, you can increase the return of investment (ROI) without having to find additional funds for a new security platform. Defender for Cloud Apps provides a single pane of glass that encompasses all your applications no matter where you are in your current cloud journey.
Should this be your first-time encountering Defender for Cloud Apps (or a CASB), there are a few basic concepts that should be understood. Some of these concepts are covered throughout this blog post; however, I want to start with a quick introduction. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, formerly Microsoft Cloud App Security (MCAS), became generally available on April 6th, 2016. During that timeframe, Defender for Cloud Apps has grown into a robust CASB. Defender for Cloud Apps is recognized as a leader by Gartner® when mapped to the Magic Quadrant. This cloud-native CASB is a very competitive product in comparison to similar tools in its category. When leveraging the Microsoft Defender suite and Azure AD, these tools work seamlessly together adding context and optimizations.
Security managers, directors, and CISOs have asked me some of the following questions in the past.
What will be the level of effort (LOE) to deploy and maintain this tool at scale while supported by current staffing?
Regarding the level of effort with deployments, Microsoft offers options right out of the box. For example, Policy templates are one of the options that can be adjusted and/or applied with very little effort. We can also find plug-and-play features available to be deployed with ease when navigating to the settings and adjusting the toggle.
Will the current security staff have to go through extensive training to gain experience that might take away from other tasks?
Regarding training objectives, Microsoft has articles pinned in many places as you move around within the portal. This makes it easy for staff to get more familiar when pulling up an article to learn more about specific setting(s) when needed.
“Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps natively integrates with leading Microsoft solutions and is designed with security professionals in mind. It provides simple deployment, centralized management, and innovative automation capabilities.” – Microsoft
When navigating to the legacy portal page, it begins at the dashboard. On the left pane you have four additional categories listed; Discover, Investigate, Control, and Alerts.
When using Defender for Cloud Apps, Application Governance is a good way of tightening controls around apps. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is an agentless CASB, meaning we utilize integrations for remediations to be actioned and the CASB itself does not have any control to govern the applications as a standalone tool. We need to keep in mind that it is not the enforcer, but rather an evaluator, letting all your other tools do the actual enforcement action.
Reviewing what integrations can be leveraged is of utmost importance when planning to govern applications. First determine what data sources can be brought in, the current identity provider(s) in use, and specific app connectors. Once in place then the governance policies will be actionable. Below there are two examples that further expand on this.
Example 1: To set up applications to be sanctioned or unsanctioned you first need to leverage your current toolsets such as a secure access service edge (SASE) solution, an edge firewall, or if using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (Microsoft native XDR), that is also an option. These data sources will action requests from an ingress/egress perspective once the signal from Defender for Cloud Apps informs to block or allow. If the goal is to utilize the sanction/un-sanction option with applications, you have to work with a specific data source that can manage the enforcement action.
Example 2: Defender for Cloud Apps Conditional Access App control apps also would need an integration for enforcement. The governance aspect in scope being access and session policies to enforce control over apps. Once again Defender for Cloud Apps will not enforce the action for that we would need to look towards an identity provider (IdP) to help us out. We know Azure AD, under the Microsoft Entra suite, is a native IdP that works directly with Defender for Cloud Apps. Within Azure AD, create a conditional access policy pointing to the custom access or session policy in Defender for Cloud Apps. This can also be deployed to on-premise applications with an application proxy in Azure AD. If another IdP than Azure AD is being utilized, then configure SAML 2.0 or OpenID Connect and connect the applications. Where the application resides, and the authoritative source for identities, will determine the specific integration parameters. Integrating these control policies will assist with tightening down the who, what, and where pertaining to your applications. Policy configurations in Defender for Cloud Apps are very granular, and depending on the use case you can set up these policies as specific or broad as you want. If you want to allow only certain users from a specific range of IP addresses to access certain applications, use access policies. If looking to limit what actions/activities are allowed, then it can be done by adding in a session policy.
Microsoft is always adding in new enhanced benefits while consolidating and integrating their tools. Defender for Cloud Apps falls under the M365 Defender suite, but as of the time of writing, it also has its own separate portal available. Some of the features are starting to populate the M365 Defender portal giving a centralized view over all your applications, endpoints, emails, and identities. There are new features and functions currently released that pertain to Application Security. Recently Microsoft added security posture management (SSPM) in preview so that customers can gauge additional visibility and remediate potential gaps within their application footprint. Microsoft has also added another layer to application governance itself releasing a new app governance add-on to provide additional control aspects to your applications. This add-on works with Azure AD and Defender for Cloud Apps to stop app usage when analyzing data usage, permissions, and anomalies pertaining to the apps in scope. Below is an architecture diagram that showcases the lifecycle this add-on delivers:
- Smart Water Detector: Our water detector alarm...
- Quick & Accurate Leak Detection: Our WWD Water...
- All-Orientation Operation: Our water sensor alarm...
- Compact & Easy to Install: Our wireless water...
- Durable & Long-lasting: is made to last, with a...
- Super Durability】10000+ flex life and double...
- Gold-plated connectors and aluminum
- ★ Surround Sound Capability ★ Truely supports...
- ★ Multi-device support ★ Compatible with...
- Super Durability】10000+ flex life and double...
- Gold-plated connectors and aluminum
- ★ Surround Sound Capability ★ Truely supports...
- ★ Multi-device support ★ Compatible with...
Last update on 2024-04-05 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Source:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/defender-cloud-apps/app-governance-manage-app-governance
In conclusion: Defender for Cloud Apps governs applications by leveraging data sources to enforce policies and settings. The features we covered include sanctioning or unsanctioning apps, setting up granular policies to define access and session perimeters using an IdP, and new add-on capabilities released providing additional control objectives on demand.
— This blog post is not meant as a configuration guide, or to fit exact scenarios as there are dependencies that could change the desired outcome which depends on a broad set of items. This is a general overview of features that is in place and currently supported by Microsoft.–
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from The Guiding Point | GuidePoint Security authored by Thomas Lysaa. Read the original post at: https://www.guidepointsecurity.com/blog/application-governance-in-the-cloud-with-microsofts-native-casb-solution/
Application governance in the cloud with Microsoft’s native CASB solution





