This article provides recommendations for building an app deployment pipeline for containerized apps on Azure Kubernetes Service hybrid deployment options (AKS hybrid). The apps can run on Azure Stack HCI or Windows Server. Specifically, the guidance is for deployments that use Azure Arc and GitOps.
Architecture

Download a Visio file of this architecture.
Workflow
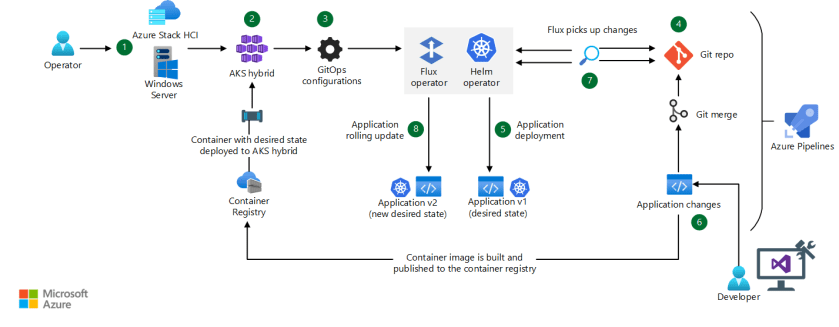
The architecture illustrates an implementation that deploys containerized applications on AKS hybrid clusters that are running on Azure Stack HCI or Windows Server. It uses GitOps to manage the infrastructure as code (IaC).
- An operator sets up an on-premises infrastructure on Azure Stack HCI or on Windows Server hardware that's capable of hosting an AKS hybrid cluster.
- On-premises, an administrator deploys an AKS hybrid cluster on the Azure Stack HCI or Windows Server infrastructure and connects the AKS hybrid cluster to Azure by using Azure Arc. To enable GitOps, the administrator also deploys the Flux extension and its configuration to the AKS hybrid cluster.
- GitOps configurations facilitate IaC. These GitOps configurations represent the desired state of the AKS hybrid cluster and use the information provided by the local administration. The local administration refers to the management tools, interfaces, and practices that are provided by the AKS hybrid cluster that's deployed on Azure Stack HCI or Windows Server.
- The administrator pushes GitOps configurations to a Git repository. You can also use a Helm or Kustomize repository. The Flux components in the AKS hybrid cluster monitor the repository for changes, detecting and applying updates as needed.
- The Flux extension in the AKS hybrid cluster receives a notification from the GitOps flow when changes are made to the configurations in the repositories. It automatically triggers deployment of the desired configuration by using Helm charts or Kustomize.
- Application changes in the form of new or updated configuration or code are pushed to the designated repositories, including corresponding container image updates. These container image updates are pushed to private or public container registries.
- The Flux operator in the AKS hybrid cluster detects changes in the repositories and initiates their deployment to the cluster.
- Changes are implemented in a rolling fashion on the cluster to ensure minimal downtime and preserve the desired state of the cluster.
Components
- Azure Stack HCI is a hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) solution that you can use to run virtualized workloads on-premises. It uses a combination of software-defined compute, storage, and networking technologies. It's built on top of Windows Server and integrates with Azure services to provide a hybrid cloud experience.
- AKS on Azure Stack HCI enables developers and admins to use AKS to deploy and manage containerized apps on Azure Stack HCI.
- Azure Arc is a hybrid cloud-management solution that you can use to manage servers, Kubernetes clusters, and applications across on-premises, multicloud, and edge environments. It provides a unified management experience by enabling you to govern resources across different environments by using Azure management services like Azure Policy, Azure Security Center, and Azure Monitor.
- Git, Helm, and Bitbucket repositories (public and private) can host GitOps configurations, including Azure DevOps and GitHub repositories.
- Container registries (public and private), including Azure Container Registry and Docker Hub, host container images.
- Azure Pipelines is a continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) service that automates updates to repositories and registries.
- Flux is an open-source GitOps deployment tool that Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters can use. You can use the Azure Arc connection to implement the cluster components that track changes to the Git, Helm, or Kustomize repositories that you designate and apply them to the local cluster. The Flux operator periodically (or based on a trigger) reviews the existing cluster configuration to ensure that it matches the one in the repository. If it detects differences, Flux remediates them by applying or, in the case of configuration drift, reapplying the desired configuration.
Scenario details
Running containers at scale requires an orchestrator to automate scheduling, deployment, networking, scaling, health monitoring, and container management. Kubernetes is a commonly used orchestrator for new containerized deployments. As the number of Kubernetes clusters and environments grows, managing them individually can be challenging. Using Azure Arc-enabled services like Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes, GitOps, Azure Monitor, and Azure Policy reduces the administrative burden and helps address this challenge.
Considerations
These considerations implement the pillars of the Azure Well-Architected Framework, which is a set of guiding tenets that can be used to improve the quality of a workload. For more information, see Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework.
The Well-Architected Framework provides guiding principles that help with assessing and optimizing the benefits of cloud-based solutions. Given the inherent integration of on-premises AKS deployments with Azure technologies, it's appropriate to apply framework recommendations to your design and implementation of GitOps.
Reliability
Reliability ensures that your application can meet the commitments you make to your customers. For more information, see Overview of the reliability pillar.
- Use the high-availability features of Kubernetes to ensure high reliability in GitOps-based solutions.
- Use Flux v2 to further increase application availability in deployments that span multiple locations or clusters.
- Use automated deployments to reduce the possibility of human error.
- Integrate a CI/CD pipeline into your architecture to improve the effectiveness of automated testing.
- Track all code changes so that you can quickly identify and resolve problems. To track these operational changes, use the built-in capabilities of GitHub or Azure DevOps. You can use these tools to implement policies and automation to make sure changes are tracked, follow the appropriate approval process, and are maintainable.
Security
Security provides assurances against deliberate attacks and the abuse of your valuable data and systems. For more information, see Overview of the security pillar.
-
Understand the security benefits of the architecture. With Flux v2, Kustomize, GitOps, and DevOps pipelines operational changes are applied via automation. You can control and audit the code that implements these operational practices by taking advantage of mechanisms like branch protection, pull request reviews, and immutable history. The IaC approach removes the need to manage permissions for accessing the infrastructure and supports the principle of least privilege. Flux support for namespace-based configuration scoping facilitates multitenant scenarios.
-
Understand encryption. To help ensure data security, the cluster configuration service stores the Flux configuration resource data in an Azure Cosmos DB database and encrypts it at rest.
-
Consider using private endpoints. GitOps supports Azure Private Link for connectivity to Azure Arc–related services.
Use Azure policies and Azure Arc
Azure Arc extends the scope of resource management beyond Azure. The extended scope provides a range of benefits that apply to physical and virtual servers. In the context of AKS, these benefits include:
- Governance. Azure Arc can enforce runtime governance that affects AKS clusters and their pods by using Azure Policy for Kubernetes and centralized reporting of the corresponding policy compliance. You can use this capability to, for example, enforce the use of HTTPS for ingress traffic that targets the Kubernetes cluster, or to ensure that containers listen only on specific ports that you designate.
- Improved operations. Azure Arc provides enhanced support for automated cluster configuration via GitOps.
Azure Policy facilitates centralized GitOps management via the built-in Deploy GitOps to Kubernetes cluster policy definition. After you assign this policy, it automatically applies any GitOps-based configuration you choose to Azure Arc–enabled Kubernetes clusters that you designate, if their Azure Resource Manager resources are in the scope of the assignment.
Cost optimization
Cost optimization is about reducing unnecessary expenses and improving operational efficiencies. For more information, see Overview of the cost optimization pillar.
-
Use the automation that GitOps provides to minimize your management and maintenance overhead. The simplified operational model requires less effort to maintain and results in reduced operational costs.
-
Use AKS hybrid. AKS hybrid provides built-in support for autoscaling the computing resources and increased workload density that's inherent to containerization. Autoscaling can help you right-size your physical infrastructure and speed up datacenter consolidation initiatives, which can help you save money.
Operational excellence
Operational excellence covers the operations processes that deploy an application and keep it running in production. For more information, see Overview of the operational excellence pillar.
-
Use GitOps repositories to provide a single source of truth that stores all AKS application and cluster infrastructure data. These repositories can serve as the only component that applies changes to the cluster.
-
Take advantage of the GitOps integration with the DevOps approach to infrastructure to shorten the time required to deliver new software releases. We also recommend that you use Azure Resource Manager and Azure Arc to build a consistent operational model for cloud-based and on-premises containerized workloads. To control GitOps configurations at different levels, use Azure Policy together with the capabilities of Flux operators. By doing so, you can establish control at the enterprise level, at the level of an individual AKS cluster, or even at the level of specific namespaces within a cluster.
-
Create GitOps configurations that are scoped to a cluster (or to multiple clusters) to implement a baseline for components of the containerized infrastructure, like ingress controllers, service meshes, security products, and monitoring solutions. Doing so can help you ensure that your clusters satisfy the baseline infrastructure requirements.
-
Create namespace-level GitOps configurations that enable you to control the resources of your workloads at a more granular level (for example, pods, services, and ingress routes), and therefore ensure that your workloads conform to application standards. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your deployment and management of AKS hybrid applications remain efficient, effective, and cost effective.
Use GitOps
GitOps is a great match for the management of AKS clusters. Kubernetes is based on the declarative model. The cluster state and its components are described in code. GitOps stores that code in a Git repository and uses it to define the desired state of the target environment.
Code changes are subject to version control, auditing, and optional reviews and approvals. You can use reviews and approvals to automatically trigger updates of the AKS infrastructure and containerized workloads. GitOps uses a pull model, in which a specialized set of cluster components polls the status of the repository. When a change is detected, an AKS-hosted GitOps component retrieves and applies the new configuration.
GitOps significantly minimizes the need for direct cluster management, resulting in a simplified operational model and also increased security. GitOps supports the principle of least privilege. For example, GitOps removes the need to modify clusters manually via kubectl, so fewer privileges are required. GitOps also provides early feedback about proposed policy changes. Early feedback is particularly valuable to developers because it helps them reduce the risk and costs that are associated with bugs.
GitOps simplifies the standardization of cluster configurations across your organization to meet compliance and governance requirements. You can define a baseline configuration that you want to apply to every cluster and its components, including, for example, network policies, role bindings, and pod security policies. To implement that configuration across all Azure Arc-enabled clusters, you can use Azure Policy, targeting resource groups or subscriptions. These policies apply automatically to existing resources and also to resources that are created after the policy assignment.
GitOps links your cluster with one or more Git repositories. You can use each repository to describe different aspects of cluster configuration. The resulting declarative model facilitates automation of the provisioning and management of Kubernetes resources like namespaces or deployments via their manifest files. You can also use Helm charts, which, together with Flux v2 and Kustomize, facilitate the automated deployment of containerized applications, or Kustomize files that describe environment-specific changes.
Use Flux
Flux is implemented as a Kubernetes operator. It uses a set of controllers and corresponding declarative APIs. The controllers manage a set of custom resources that work collectively to deliver the intended functionality.
GitOps is enabled in an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster as a Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions/microsoft.flux cluster extension. After you install the microsoft.flux cluster extension, you can create one or more fluxConfigurations resources that sync the content of configuration sources to the cluster and reconcile the cluster to a desired state.
- Purposeful Design: Travel with ease and look great...
- Ready-to-Go Performance: The Aspire 3 is...
- Visibly Stunning: Experience sharp details and...
- Internal Specifications: 8GB LPDDR5 Onboard...
- The HD front-facing camera uses Acer’s TNR...
- 【14" HD Display】14.0-inch diagonal, HD (1366 x...
- 【Processor & Graphics】Intel Celeron N4120, 4...
- 【RAM & Storage】8GB high-bandwidth DDR4 Memory...
- 【Ports】1 x USB 3.1 Type-C ports, 2 x USB 3.1...
- 【Windows 11 Home in S mode】You may switch to...
By default, the microsoft.flux extension installs the Flux controllers (Source, Kustomize, Helm, and Notification) and FluxConfig Custom Resource Definitions (CRD), fluxconfig-agent, and fluxconfig-controller. You can also choose which of these controllers you want to install and can optionally install the Flux image-automation and image-reflector controllers, which facilitate updating and retrieving Docker images.
When you create a fluxConfigurations resource, the values you supply for the parameters, like the target Git repository, are used to create and configure the Kubernetes objects that enable the GitOps functionality on the cluster.
When you deploy and configure Flux v2 cluster extensions, it provides the following components and functionality:
source-controller. Monitors sources of custom configurations, such as Git repositories, Helm repositories, and cloud storage services like S3 buckets, and synchronizes and authorizes against these sources.kustomize-controller. Monitors custom resources that are based on Kustomization CRDs, which contain Kubernetes manifests and raw YAML files. Applies the manifests and YAML files to the cluster.helm-controller. Monitors custom resources that are based on charts and stored in Helm repositories surfaced bysource-controller.notification-controller. Manages inbound events that originate from a Git repository and outbound events, like those that target Microsoft Teams or Slack.FluxConfig CRD. Represents custom resources that define Flux-specific Kubernetes objects.fluxconfig-agent. Detects new and updated Flux configuration resources. Initiates the corresponding configuration updates on the cluster. Communicates status changes to Azure.fluxconfig-controller. Monitorsfluxconfigscustom resources.
Version 2 of Flux provides these additional features:
| Category | Feature |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure and workload management | Deployment dependency management |
| Integration with Kubernetes role-based access control (RBAC) | |
| Health assessments for clusters and their workloads | |
| Automated container image updates to Git, including image scanning and patching | |
| Interoperability with Cluster API providers | |
| Security and governance | Alerting to external systems (via webhook senders) |
| Policy-driven validation, including support for Open Policy Agent Gatekeeper | |
| Container image scanning and patching | |
| Alerting to external systems (via webhook senders) | |
| Integration with other GitOps flows | Integration with a range of Git providers, including GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket |
| Interoperability with workflow providers, including GitHub Actions |
For more information, see GitOps Flux v2 configurations with AKS and Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes.
Performance efficiency
Performance efficiency is the ability of your workload to scale to meet the demands placed on it by users in an efficient manner. For more information, see Performance efficiency pillar overview.
Cluster workloads benefit from the scalability and agility that's inherent to the Kubernetes platform. Flux v2 offers additional agility, reducing the time required for end-to-end software delivery.
-
Optimize your Kubernetes cluster and infrastructure setup for your specific workloads. We recommend that you work with the application developer to determine the required settings.
-
Use the autoscaling feature in Kubernetes. For more information, see Cluster autoscaling in AKS hybrid.
-
Add a cache to optimize the application.
-
Establish a performance baseline. Benchmark your architecture and use metrics and monitoring tools to identify any problems or bottlenecks that affect performance.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal authors:
Other contributors:
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- EFFICIENT PERFORMANCE: Equipped with 4GB...
- Powerful configuration: Equipped with the Intel...
- LIGHTWEIGHT AND ADVANCED - The slim case weighs...
- Multifunctional interface: fast connection with...
- Worry-free customer service: from date of...
- Powered by an Intel Core i5 13th Gen 13420H 1.5GHz...
- Equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050 6GB GDDR6...
- Includes 8GB of DDR4-3200 RAM for smooth...
- Features a spacious 512GB Solid State Drive for...
- Boasts a vibrant 15.6" FHD IPS Micro-Edge...
- Processor - Powered by 11 Gen i5-1145G7 Processor...
- Memory and Storage - Equipped with 16GB of...
- FHD Display - 15.6 inch (1920 x 1080) FHD display,...
- FEATURES - Intel Iris Xe Graphics – Audio by...
- Convenience & Warranty: 2 x Thunderbolt 4 with...
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/example-scenario/hybrid/aks-hybrid-stack-hci